Monitoring Indoor Air Quality
People spend up to 90% of their time indoors and breathe in thousands of liters of air each day. Maintaining
good indoor air quality is therefore crucial.
However, improving indoor air quality is more than just enhancing comfort — it’s about protecting health,
ensuring
overall well-being, boosting productivity, improving energy efficiency and reducing airborne contaminants.
What is Indoor Air Quality?
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the quality of the air inside buildings or structures, particularly in relation to the health and well-being of the occupants. IAQ involves the concentration of chemical and biological air pollutants and is influenced by environmental factors such as temperature and relative humidity. Proper ventilation plays a major role in maintaining good IAQ as it ensures fresh air circulation and helps control airborne pollutants and indoor climate conditions.
One single person inhales about 10 000 to 15 000 liters of air a day!
Why is it important to control indoor air quality?
The concept of indoor air quality is supported by 4 key pillars:
COMFORT & HEALTH
Spend time indoor safely...
Considering the fact that people nowadays spend
more
than 85% of their time indoors, it is essential to monitor and maintain a good indoor air quality. A
comfortable indoor climate supports the well-being and health of the occupants, improves overall
satisfaction and contributes to productivity.
EFFICIENCY & ECONOMY
Prevent unnecessary expenses...
Poor indoor air quality eventually leads to
concentration problems, learning difficulties and lower
productivity
which in turn leads to additional costs for companies, health insurance funds and society. It is a
challenge to
ensure good indoor air quality while minimising energy losses.
VIRAL CONTAMINATION
Lower the risk of viral infections...
Viruses spread via droplets and airborne
aerosols. Therefore, the risk of viral infections is much
higher in
crowded and poorly ventilated spaces. Proper ventilation reduces indoor airborne contaminants
through
air
exchange and filtration.
INFORMATION & GUIDELINES
Comply with applicable legislation...
Information and guidelines regarding
the
composition and maintenance of a good indoor air quality
are
provided
by several (inter)national organisations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the European
Commission
(EC) and local governments.
AIR
QUALITY
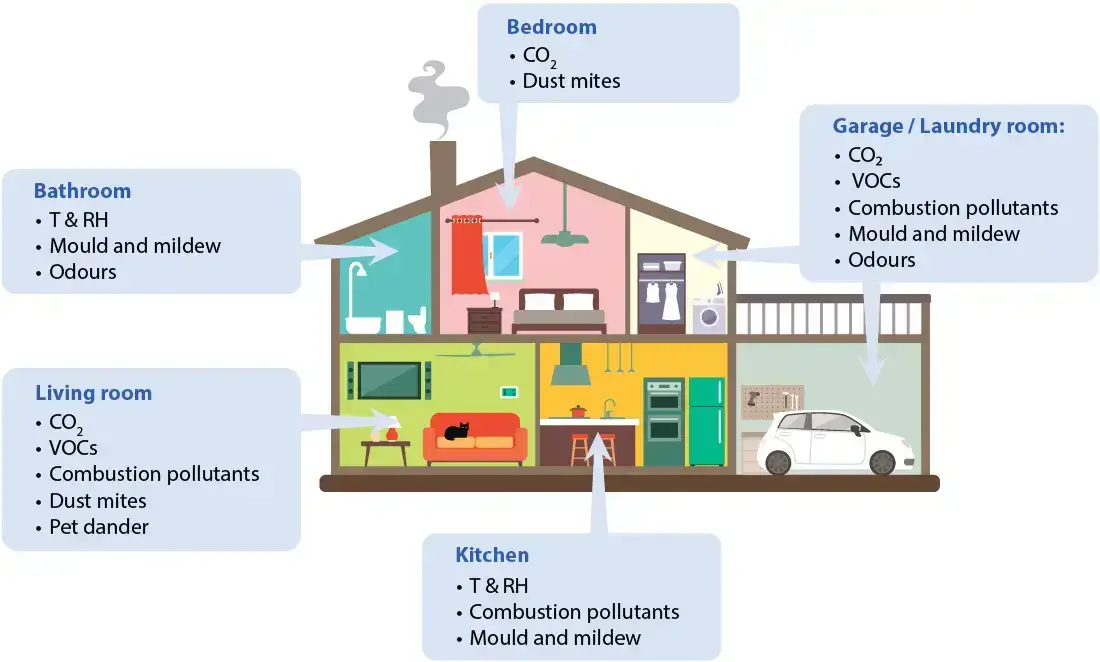
What are the main factors that determine indoor air quality?
Temperature and humidity
An inadequate temperature (T) and relative humidity (RH) not only cause discomfort, these factors also influence and aggravate each other's effects.
Air pollutants
Indoor and outdoor air pollutants include carbon dioxide (CO2), combustion contaminants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter and tobacco smoke. Chemical pollutants arising from indoor sources include Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from carpeting, cleaning agents, paints, glue, varnishes etc. Biological pollutants include bacteria, viruses, moulds and allergens such as dust mites, pet dander and pollen.
Ventilation
One of the most important factors determining indoor air quality is ventilation. As buildings become more thermally insulated, the importance of intelligent ventilation systems is growing, ensuring optimal indoor air quality while minimising energy loss.